Home > Resources > Newsletters > The AI Vue
9th January 2025
Breaking grid
Like Prometheus's fire, AI is a gift that lights the way forward but threatens to burn if wielded without care. Use it, but only when its spark is truly needed. For all else, simpler methods can be your guide.

AI is being heralded as the technology of the future, promising to revolutionize industries, streamline workflows, and create unprecedented efficiencies. However, beneath its potential lies a critical challenge: its insatiable appetite for energy.
Watts on
The promise of commercial AI hinges on creating efficiencies, doing more with less. Therein, however, lies a paradox: the more AI advances, the more energy it consumes. Here are some eye-popping stats:
- Generative AI is projected to consume a staggering quarter of all electricity in the United States by 2030 (Arm Holdings).
- Training OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4 required the energy equivalent of powering 50 American homes for 100 years.
- A single query summarizing the financial reports of the world’s public companies could cost between USD 2,400 and USD 223,000 (The Economist). “Inference”—the process of running AI models to provide outputs—is poised to surpass training in cost.
Contrast this with the human brain operating at an extraordinary level of computational efficiency, performing parallel calculations using just 20 watts of power. Replicating the brain’s functionality through neural networks requires 8 megawatts of power—400,000 times more than the brain. This disparity underscores the urgent need for innovations in AI hardware and energy management. Without breakthroughs in energy efficiency, Generative AI risks becoming economically unsustainable.
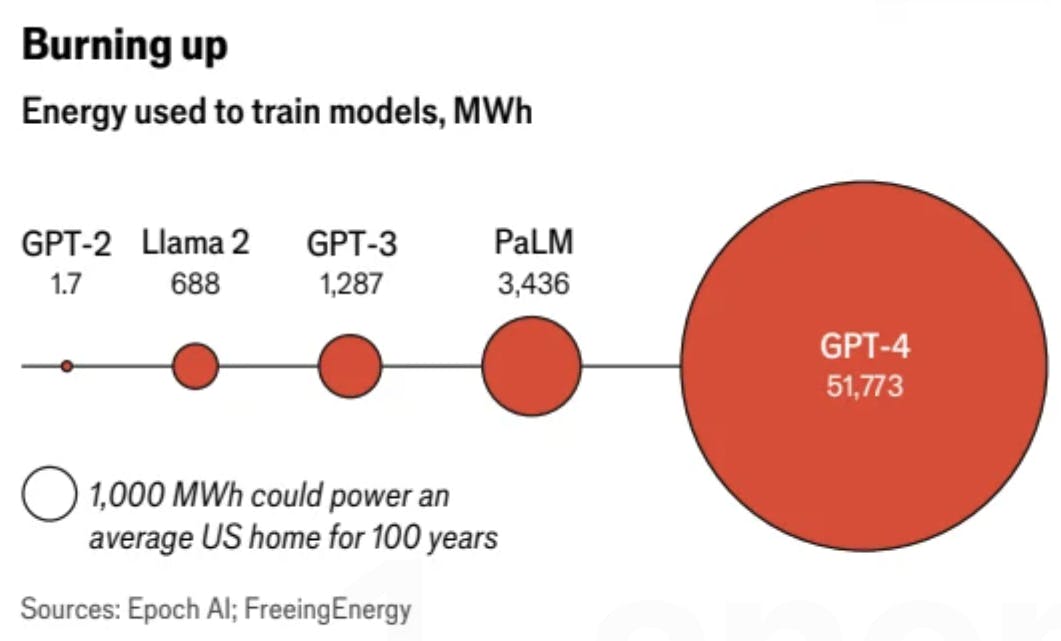
The Economist, 21-Sep-2024
From Graphics PUs to Green PUs
The semiconductor industry is racing to address AI’s energy problem. While setting up a semiconductor fabrication plant in the 1960s would have cost in the range of USD 31M (in today’s money), the fabs that TSMC is building in Arizona are estimated to be USD 20B each.
There is, however, work being done in addressing this problem.
- In modern GPT models, around 90% of inference time is attributed to data shuttling during inter-chip and intra-chip transmissions. Innovations like FinFETs, multi-core processors, and specialized AI chips such as GPUs and TPUs have improved efficiency.
- Google's TPUs address this by minimizing the transmission trips, cutting down both output time and energy consumption.
- Similarly, IBM’s NorthPole chip represents a breakthrough by eliminating off-chip memory, claiming to be 25 times more energy efficient and 20 times faster than traditional AI accelerators.
However, as chips shrink to two- and three-nanometer nodes, their thermal properties create new challenges. Heat dissipation from the chip stacks—enough to warm up the swimming pools at the Paris Olympics— is becoming a bottleneck for further advancements, necessitating additional innovations such as immersion cooling oil baths that roughly halve the carbon emissions or hoisting data centers way up in space – the final frontier, so to speak.
Little black box, big carbon footprint
Data centers, the backbone of AI, are an energy-intensive industry unto themselves. In 2023, they accounted for 4% of electricity consumption in the United States, a figure that could rise to as much as 9% by 2030. Beyond electricity, data centers use significant amounts of water to cool their servers; a batch of 25–50 AI prompts can evaporate up to half a liter of water.
Until now, the AI systems needed to train new AI models could fit into existing data centers. But in the coming times, the models could see a 10-fold rise in bandwidth necessitating the building of new data centers.
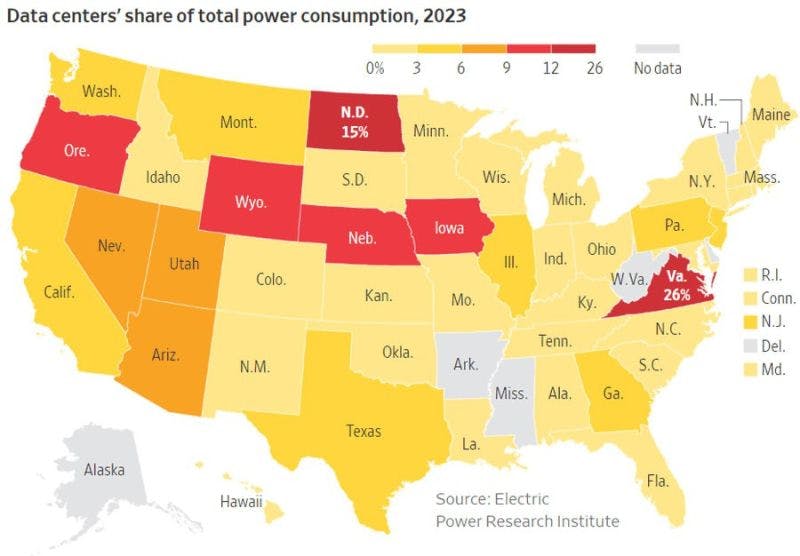
The rapid growth of AI models is pushing data centers to their limits. In cities like Atlanta, data-center construction has surged, with power capacity increasing by 76% in just the first half of 2024. However, this growth has sparked debates about property usage and environmental impact, as communities push back against the sprawl of these facilities.
Watt goes around comes around
To meet AI’s growing energy demands, companies are turning to alternative energy sources. AWS and Microsoft recently acquired nuclear-powered data centers, signaling a shift toward more sustainable, long-term solutions. Meanwhile, China is leading the world in renewable energy installations, adding five times the wind energy capacity of all G7 nations combined in 2023. Despite his calling the Inflation Reduction Act a scam, President-elect Trump’s extension of tax credits to wind and solar projects during his first term and his choice of pro-renewable-power Secretaries for the Interior and Energy departments for his next innings raises hopes that the US government would continue to support alternative energy generation.
Balancing regulation and innovation
Addressing AI’s energy challenge requires not just technological innovation but also thoughtful regulation. AI operates as infrastructure, shaping collective behaviors and requiring mechanisms to manage potential abuses. Policymakers must strike a balance between fostering innovation and mitigating the upstream and downstream effects of AI on adjacent industries.
Some experts advocate for regulatory frameworks based on periodic audits and outcome-based assessments, rather than holding developers solely accountable for unintended consequences. Such approaches could ensure that AI development remains aligned with societal goals without stifling innovation.
Think different, compute efficient
AI’s energy demands present a critical challenge that cannot be ignored. Addressing this issue will require a multi-faceted approach: advancing hardware innovations, investing in sustainable energy sources, and enacting forward-thinking regulation. As cool and fun as Large Language Models are, the development of less energy-intensive Small Language Models that are tailor-made to address specific applications is more likely to be optimal and productive for enterprises.
And, so...
AI is Prometheus's fire, a gift that lights the way forward but threatens to burn if wielded without care. Use it, but only when its spark is truly needed. For all else, simpler methods can be your guide—solutions that illuminate without scorching the earth.
About: Vue.ai is an AI orchestration platform that actively caters to enterprises in retail, BFSI, logistics, healthcare and other domains. Deploying a mixture of expertise in various AI techniques and on platforms like AWS, Azure and GCP, Vue.ai charts productive digital transformation journeys for clients across continents.
- Enterprises deploy too many single-purpose applications that cannot easily communicate with each other in their workflow, creating a disjointed system.
- An overabundance of data science and machine learning tools makes it challenging to maintain models efficiently, leading to high operating costs. Creates tension between data- and model-centric approaches.
- Massive economic costs associated with broken data cost organizations trillions in unnecessary losses. Who'd want to be a data janitor, huh!